What is oral cancer?
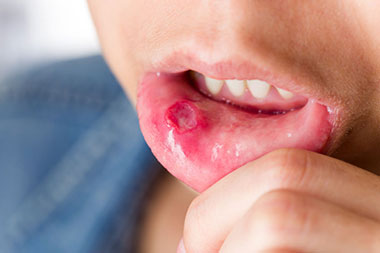 Simply put, oral or mouth cancer develops in various parts of the mouth and nearby areas, including tonsils, salivary glands, the back of the throat, and the neck lymph nodes. Men, mostly above the age of 40 remain more vulnerable to this medical condition as per multiple studies.
Simply put, oral or mouth cancer develops in various parts of the mouth and nearby areas, including tonsils, salivary glands, the back of the throat, and the neck lymph nodes. Men, mostly above the age of 40 remain more vulnerable to this medical condition as per multiple studies.
Early signs of oral cancer
The most commonly reported signs of this medical condition are red and white or velvety white patches that develop in various parts of the mouth. The patient may also notice rough spots, ulcers, lumps or bumps on the lower lip, ear pain, along with difficulty in swallowing, chewing, and moving the tongue as well as the jaw.
Some of the severe symptoms include a constant feeling of pain, numbness, and unexplained bleeding inside the mouth. If patches or rough spots do not stop bleeding within two weeks, the patient must visit a dentist or physician without wasting any more time.
Oral cancer causes
Several studies have linked the consumption of cigarettes and tobacco products to this medical condition. It is a well-proven fact that the risk of mouth cancer can be significantly reduced by maintaining oral hygiene, avoiding smoking cigarettes, cigars, tobacco (including smokeless), and alcohol consumption.
Unfortunately, non-smokers and non-drinkers are not safe either. Research suggests that around 25 percent of mouth cancer patients happen to be occasional drinkers or smokers. People with a family history of cancer and those who have excessive exposure to the sun also remain vulnerable.
Oral cancer stages
After detecting the presence of the actual cancerous tumor, doctors need to determine the stage of its development as per universally set protocol.
The cancerous tumor may initially appear like a tiny red, white spot. Unfortunately, most of the patients start looking at it as something serious when it stays in place for more than a month.
During stage 0, the disease symptoms can be found on the lips and mouth. It does not spread beyond these areas. Further, in phase 1, the tumors can grow max up to 2 CM. The cancer tumors detected in stage II are often found to be around 2 centimeters. The disease does not spread to the lymph nodes in this stage.
In stage III, the tumor may turn up to 4 centimeters in size. The disease remains restricted to only one lymph node and side of the neck where cancer initially developed.
In stage IV, besides spreading in the oral cavity and lip tissues, the disease reaches more than one lymph node on the neck. The tumor size in this stage might be 6 centimeters. The medical condition turns too complicated at this stage as the tumor reaches blood vessels, the lower jaw, or even the base of the skull. It turns into metastatic oral cancer, with the ability to spread further to the lungs, liver, and various bones in the body.
Some physicians also prefer to describe it as a local, regional, and distant stage. Local refers to the area of origin, regional indicates nearby parts, while distant means the disease has managed to spread across various parts of the body.
Dentists are trained to conduct oral screening. It involves an examination of the mouth for checking discolored tissues and lumps in the mouth. In case of anything suspicious, including tumors, the dentist may recommend a biopsy or tests to determine the nature of the concerned tumor.
Prevention of oral cancer
As mentioned earlier, avoid smoking, chewing tobacco products, and consumption of alcoholic drinks to prevent mouth cancer. Opt for a balanced diet. It must contain plant or animal-based protein, whole grains, healthy fats, and vegetables.
Avoid exposing the skin to direct sunlight, and use UV-A/B-blocking lotions whenever possible. Conduct self-examination once a month and look for unusual signs in the mouth. Plus, opt for regular dental checkups, and oral cancer screening. Unfortunately, early symptoms of oral cancer often go unnoticed, and patients approach their dentist only after the tumor attains a significant size.
Types of oral cancer
Oral cancer is classified into multiple types like lip, tongue, hard palate (on the roof of the mouth), inner cheek, gum, and floor of mouth cancer.
The oral cancer tongue involves the development of tumors, and sore or oral cancer lesions on the tongue surface while oral cancer under the tongue shows signs like sores and red and white patches that bleed at times. The (Human papillomavirus) HPV oral cancer is the type that develops in the back of the throat.
Can oral cancer be cured?
Of course, the medical condition can be cured if detected and treated at an early stage. Depending on the sub-type, stage, and severity of the tumor, the doctor would suggest tumor removal surgery, medication, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, supportive care, and radiation treatment or a combination of two of them. However, the five-year survival rate depends on how much the tumor has developed and spread.
Thanks to the advancement in medical science, drug makers are set to introduce Band-Aid-like patches to treat cancerous tumors inside the mouth. Created using nanotechnology, the piece releases drugs right on the infected cells instead of targeting the healthy ones. The patches are still in the clinical trial stage, but they offer a ray of hope for individuals who wish to avoid the side effects of chemotherapy.
Can the disease come back after treatment?
Cancer turns difficult to cure after reaching advanced stages. The possibility of recurrence also remains high. The doctor treating the cancerous tumor would be able to judge the chances of recurrence and recommend tests, and checkups from time to time after treatment. Unfortunately, there’s no sure-shot treatment to avoid recurrence. It may not come in the same place where it occurred earlier and can occur in a completely different part of the body. Thus, even after treatment, the patient needs to continue remaining under a physician’s supervision for a few days.
You can always make an appointment at Roswell, GA based TruCare Dentistry for mouth cancer screening and tests.
